 Every programmer worth his salt has written a raytracer of some sort. It’s one of the classic “recursion exercises”, with a fair amount of math to wrap your head around. I’m not interested in writing one to run on the PC – there are already far more capable ones that can run on pretty much any hardware, complete with optimizations and features I couldn’t hope to implement in my lifetime.
Every programmer worth his salt has written a raytracer of some sort. It’s one of the classic “recursion exercises”, with a fair amount of math to wrap your head around. I’m not interested in writing one to run on the PC – there are already far more capable ones that can run on pretty much any hardware, complete with optimizations and features I couldn’t hope to implement in my lifetime.
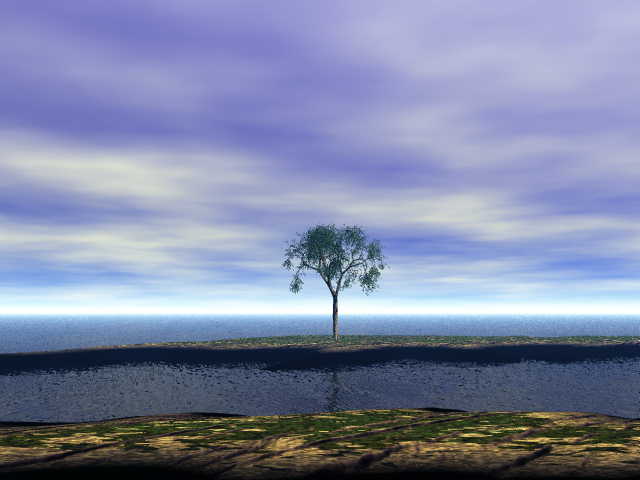
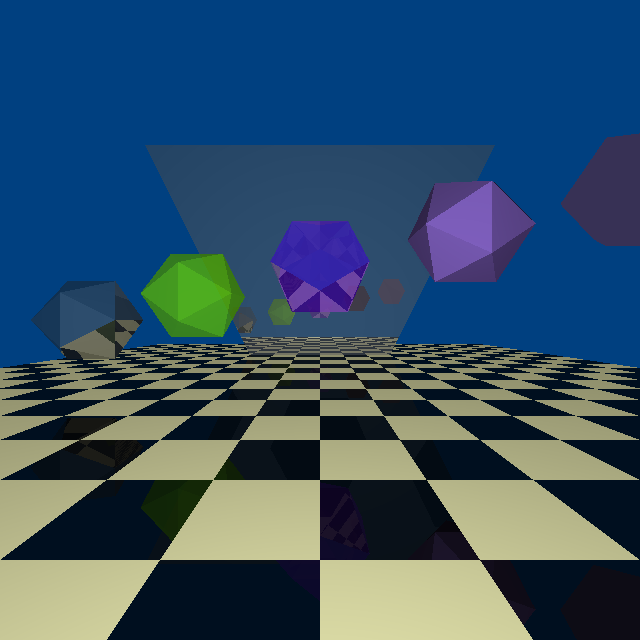
Instead, I decided to write a raytracer which targets the Atmega 328 microcontroller in my Arduino! In the end, I succeeded in banging one together that calculates ray-triangle intersection, and each triangle can have a material attached with ambient / diffuse / transparent / reflective values and an RGB color. The scene is compiled in with a .h file (stored in PROGMEM), and outputs a PPM image pixel-by-pixel over the serial port.
The same engine can be used on the PC with a few modifications, so I was able to benchmark the performance of the Arduino in comparison with a modern laptop. The “detailed scene” rendered a 640×640 image in 263 seconds on the laptop. The same scene, scaled to only 64×64, still took 4008.471 seconds… in other words, the PC outperformed the Arduino by a factor of ~1500.
 I posted the code, and further write-up, on the Arduino.cc message board at this link: http://forum.arduino.cc/index.php?topic=281076.0. There are a lot of features that COULD be added here, but none that I actually intend to do. If I need a raytracer in the future, I’m just downloading POVRay : )
I posted the code, and further write-up, on the Arduino.cc message board at this link: http://forum.arduino.cc/index.php?topic=281076.0. There are a lot of features that COULD be added here, but none that I actually intend to do. If I need a raytracer in the future, I’m just downloading POVRay : )